欢迎您访问52ij英汉互译网,今天小编为你分享的英语知识是:【冥王星变色 原因疑为季节变化所致】,下面是详细的分享!
冥王星变色 原因疑为季节变化所致

New Pluto Pictures Unveiled; Hubble's Sharpest Yet
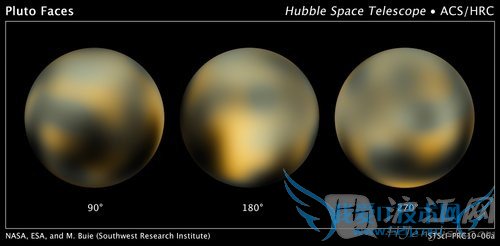
Swaths of white, dark orange, and charcoal gray dance across the surface of Pluto in the sharpest view yet of the dwarf planet, made possible by pictures from the Hubble Space Telescope.
The new Hubble shots, taken from 2002 to 2003, show rapid changes on Pluto's surface driven by the world's extreme seasons, lead investigator Marc Buie, of the Southwest Research Institute in Boulder, Colorado, said today at a press briefing.
In a project that took four years and 20 computers running simultaneously, Buie and colleagues combined 384 Hubble pictures of Pluto to create what he calls "my best guess at a true-color appearance" for the tiny world.
"If you were sitting in a spacecraft puttering around Pluto and looking out the window, this is what you'd see, but in higher resolution."
The pictures reveal that Pluto is a much more dynamic body than commonly thought, and they offer astronomers ideas of what to focus on when the New Horizons spacecraft reaches the dwarf planet in 2015.
Pluto at Its Most Extreme
As seen in the new pictures, Pluto's orange and gray hues could be the result of methane on the surface being broken down by sunlight, leaving a carbon-rich residue, the scientists say. (Related: "Pluto Has 'Upside Down' Atmosphere.")
While the Hubble pictures aren't detailed enough to make out surface features, the striking differences in dark and bright regions suggest that Pluto has highly diversified terrain.
And by comparing the new pictures to previous images, astronomers can tell that some parts of Pluto, including the southern hemisphere, became significantly darker and redder between 2000 and 2002, while the northern hemisphere got brighter.
It's likely these changes are due to ice melting and refreezing as Pluto's seasons change, astronomer Mike Brown, of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, said at the briefing.
Pluto takes about 248 years to make a full orbit around the sun, traveling on an extremely elliptical path in a region of the solar system called the Kuiper belt.
Pluto's elongated orbit means that at its closest, the tiny world gets about 2.7 billion miles (4.4 billion kilometers) from the sun, while at its farthest Pluto is about 4.5 billion miles (7.3 billion kilometers).
Such extreme swings cause Pluto's surface to undergo the most dramatic changes of any known body in the solar system, Brown said.
"Places that have weather change dramatically, because it's easy to blow things around," Brown said, referring to the constant changes seen on planets with atmospheres, such as Jupiter and Saturn. "But rapid surface changes are more rare."
When Pluto goes from spring to fall, "it's as if on Earth you had a nice springtime day of 60 or 70 degrees [Fahrenheit, or 15.5 to 21 degrees Celsius] and in the fall ... it dropped to something like -90 degrees [Fahrenheit, or -67.7 degrees Celsius]," he said. "It's a ridiculously extreme place to be."
New Horizons Getting Closer to Pluto
Hubble's latest Pluto pictures were actually taken by older cameras on the recently upgraded space telescope. Following the installation of the Wide Field Camera 3 in 2009, Hubble can now be used to take even more detailed pictures of Pluto. (See some of the first pictures taken by the newly upgraded Hubble.)
But the best Pluto portraits are likely to come from New Horizons. Launched in 2006, the probe is more than halfway to Pluto and is due to be the first spacecraft to orbit the dwarf planet, offering new insights into the largely mysterious objects that exist in the Kuiper belt.
"Pluto isn't the biggest thing out there," Brown noted.
"But it is the closest ... and it is going to be the one we learn the most about to help us interpret all the other things in the outer solar system."
相关中文报道(摘自腾讯科技)
在美国宇航局“新地平线”探测器飞越冥王星表面执行为期6个月的勘测活动之前,哈勃望远镜仅拍摄到冥王星的轮廓图像,目前哈勃望远镜拍摄到的这些珍贵图像资料将有助于新地平线探测器2015年飞越冥王星表面揭示其神秘谜团。
冥王星是颇受天文学家关注的星体,由于它体积很小,并且距离遥远,它是很难被观测的。哈勃望远镜能够观测到冥王星表面数百公里范围的表面状况,但这对于理解冥王星表面地质情况非常模糊。对于冥王星表面的色彩和亮度,哈勃望远镜揭示出复杂的表面结构,显示冥王星表面带有白色、黑色、橙色和黑巧克力色斑驳状地形颜色。这些复杂表面颜色的形成是由于太阳紫外线辐射分解冥王星表面甲烷,从而在表面残留黑红色含碳剩余物质。
2002年至2003年拍摄的冥王星照片与1994年的哈勃望远镜拍摄照片相对比,天文学家发现冥王星北极地区变得更加明亮,而南极地区变得更黑暗。这些变化暗示着冥王星表面可见形态存在着非常复杂的进程,并且最新观测数据将用于后期的研究工作。
这些图片可以使行星天文学家更好地解释过去三十多年来其他望远镜的观测结果,美国科罗拉多州西南研究协会首席调查员马克-布西(Marc Buie)说:“哈勃望远镜的观测结果至关重要,它可以将之前科学家对冥王星的观测疑点进行综合解释,并显示出冥王星气候和季节性变化的关联性,这将开启冥王星研究的新线索。”
哈勃望远镜的这些观测图片强调出冥王星并不仅仅是一个冰冻岩石球态星体,它是一颗具有大气层显著变化的“动态世界”。冥王星表面颜色的差异是由该星体轴倾斜影响248年为周期的椭圆形轨道变化从而驱动季节性变迁,这一点与地球不相同,地球轴倾斜只影响季节变化。由于冥王星的轨道呈椭圆形,它的季节性变化非常不均匀,当冥王星接近太阳时它将沿着轨道更快速地移动,使得北半球极地从春季过渡至夏季很短暂。
1988-2002年间的地面观测数据显示,该时期内冥王星大气层质量增加一倍。这可能是由于氮冰加热升华进入大气层造成的,2002-2003年哈勃望远镜的最新观测结果表明,这些图像资料将为天文学家如何理解冥王星季节变化和其大气层变化趋势提供至关重要的线索。
目前,哈勃望远镜最新拍摄的这些图像对于2015年新地平线探测器飞越冥王星计划将提供宝贵的图像资料,预计新地平线探测器将很快地飞越冥王星一个半球表面,并尽可能多地获得冥王星表面地质状况信息。哈勃望远镜所拍摄到的一处亮点暗示着该处含有大量的一氧化碳冰霜,这将成为新地平线探测器的首选勘测目标,该探测器将进一步观测发亮区域与周边覆盖着漆黑表面物质之间的分界线。
目前,哈勃望远镜最新的冥王星照片将发表在3月份出版的《天体物理学杂志上》。
- 评论列表(网友评论仅供网友表达个人看法,并不表明本站同意其观点或证实其描述)
-
