对java接触比较深的人都知道,java.util.ArrayList是由Array实现的。但ArrayList与Array最显著的差别就是,数组的长度在初始化时固定的,ArrayList在add时理论上讲是无限的(会根据性能,存储合理的数据量)
本文就是通过源码,来解析java.utilArrayList如何来实现可以添加无限数据
前期准备工作(包括相关工具或所使用的原料等)Javajava.util.ArrayList 详细的操作方法或具体步骤
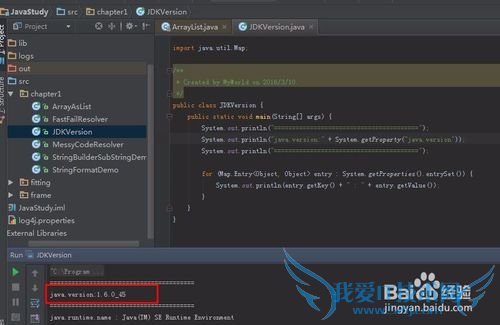
本文使用的JDK版本:
java.version:1.6.0_45
获取JDK版本的API:
System.getProperty("java.version")
源码分析:
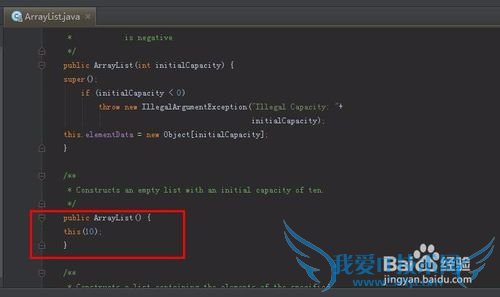
使用无参构造函数初始化时,java.util.ArrayList调用了另外一个构造函数
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
this(10);
}
源码分析:
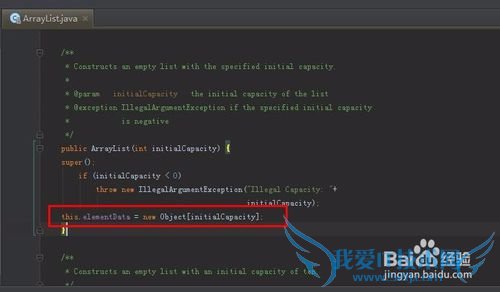
构造函数public ArrayList(int initialCapacity)示例:
/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list
* @exception IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity * is negative
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity);
this.elementData=new Object[initialCapacity];
}
源码分析:
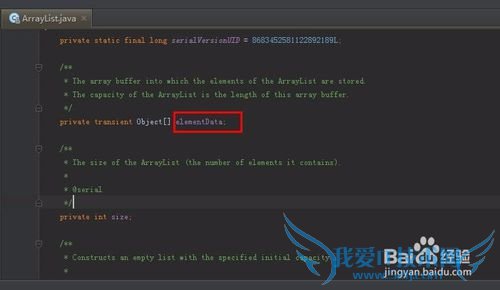
elementData是什么,是数组,
看来传说是真的:ArrayList的确是使用Array来存储数据的
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer.
*/
private transient Object[] elementData;/**
* The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).
*
* @serial
*/private int size;
问题来了,java.util.ArrayList在new时明明只分配了长度为10的数组,为什么在实际操作中貌似可以添加任意多的数据呢
看看常用的add方法:
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return true (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacity(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++]=e;
return true;
}
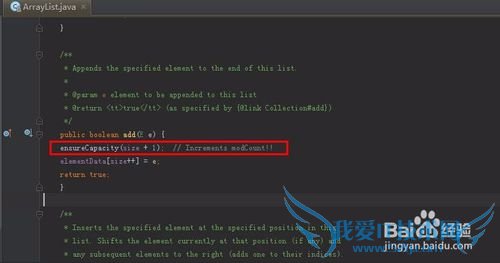
add方法中除了调用ensureCapacity是黑洞外,其它的几行,木有发现能让add无限进行下去的原因
看看ensureCapacity,传的参数是当前存储元素个数,再加1:
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
int oldCapacity=elementData.length;
if (minCapacity > oldCapacity) {
Object oldData[]=elementData;
int newCapacity=(oldCapacity * 3)/2 + 1;
if (newCapacity < minCapacity)
newCapacity=minCapacity; // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData=Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
}
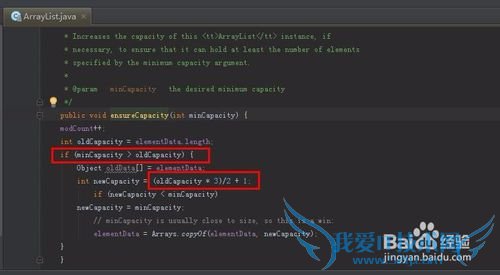
总结:
已经知道了java.util.ArrayList是使用Array来存储数据,
使用无参构造函数分配的存储数据的数组长度是10
每接近一次elementData.length,进行按照当前数组长度的1.5倍进行分配内存大小,并进行将数据从一个数组copy到新数组的操作
优化建议来了:
如果预先可以知道或大致知道,需要存储到java.util.ArrayList的数据量,可以使用public ArrayList(int initialCapacity)来进行初始化
当然把入参initialCapacity稍等设大点,也可以。
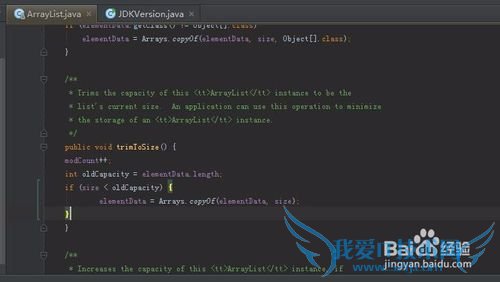
如果觉得分析的内存过多,试试ArrayList的trimToSize方法
- 评论列表(网友评论仅供网友表达个人看法,并不表明本站同意其观点或证实其描述)
-
