Java中读取文件的方式多种多样,由于经常读写小文件,在这里简单介绍下几种方式。
前期准备工作(包括相关工具或所使用的原料等)jdkeclipse除此之外不需要其他的jar包 详细的操作方法或具体步骤
预处理文件。这里有三种格式的源文件。包括
1. 占用空间117M,大小70.1M的21471个小文件组成的文件夹
2. 上述小文件通过zip格式压缩后形成的zip文件,大小33.9M
3. 上述小文件写在一个文件中后的一个大文件70.3M(每个文件占用两行,第一行为文件名,第二行为文件内容)
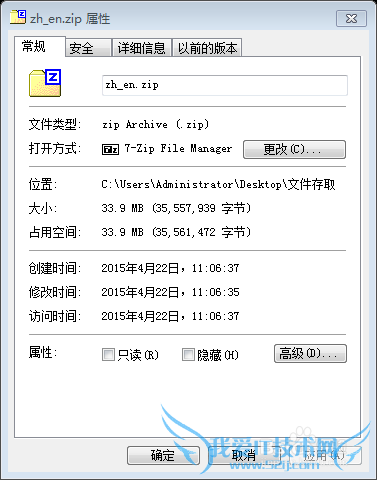
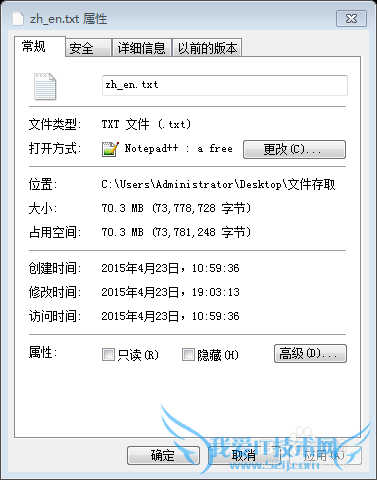
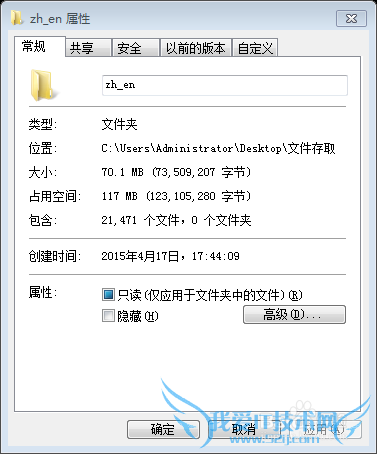
分别通过默认的带有Buffer的字节输入流与字符输入流来读取三种格式的文件。(缓冲区使用默认的8k,参考资料中说明了8k是一个综合效果较好的缓冲区大小)。代码在下一个“代码”部分。
下面是结果示例,可以看到
1. 字节流明显比字符流有更快的速度,只是有时候可能需要使用字符流来方便进行人机交互。
2. 小文件由于打开IO频繁,其效率是最慢的
3. 带有Buffer的大文件是其中速度最快的,但是由于将多个文件组合在一个文件中,这个就需要自己设置分割方式,以及区分的办法了
4. zip文件居中
5. 在本次实验中对于字节流的读写,速度大概是1:10:100的比例
对于字符流的速度大约是1:4:20的样子

代码
三种格式文件读取代码:
public static File[] get()//读取一个大文件
{
return new File[]{new File("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/文件存取/zh_en.txt")};
}
public static File [] get()//读取多个小文件
{
return new File("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/文件存取/zh_en").listFiles();
}
public static ZipInputStream get() throws IOException//读取zip文件
{
return new ZipInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/文件存取/zh_en.zip"))));
}
zip文件测试
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
System.out.println("StrTime\t" + Time());
System.out.println("StreamTime\t" + Time2());
}
private static long Time() throws IOException
{
ZipInputStream zis=GiveFiles.get();
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
int all=0;
ZipEntry entry;
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(zis));
while ((entry=zis.getNextEntry()) !=null)
{
if(!entry.isDirectory())
{
String line="";
while((line=br.readLine()) !=null)
{
all +=line.length();
}
}
zis.closeEntry();
}
br.close();
zis.close();
System.out.println(all);
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
private static long Time2() throws IOException
{
ZipInputStream zis=GiveFiles.get();
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
int all=0;
ZipEntry entry;
while ((entry=zis.getNextEntry()) !=null)
{
if(!entry.isDirectory())
{
byte [] temp=new byte[1024];
int length=0;
while((length=zis.read(temp)) > 0)
{
all +=length;
}
}
zis.closeEntry();
}
zis.close();
System.out.println(all);
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
多个小文件测试
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
System.out.println("StreamIOFilesTime\t" + StreamIOFilesTime());
System.out.println("StrIOFilesTime\t" + StrIOFilesTime());
System.out.println("RandomIOFilesTime\t" + RandomIOFilesTime());
}
private static long RandomIOFilesTime() throws IOException
{
File [] files=GiveFiles.get();
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
int all=0;
for (File file : files)
{
byte [] temp=new byte[1024];
int length=0;
RandomAccessFile rfile=new RandomAccessFile(file, "r");
while((length=rfile.read(temp)) > 0)
{
all +=length;
}
rfile.close();
}
System.out.println(all);
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
private static long StreamIOFilesTime() throws IOException
{
File [] files=GiveFiles.get();
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
int all=0;
for (File file : files)
{
int length=0;
BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
byte [] temp=new byte[1024];
while((length=bis.read(temp)) > 0)
{
all +=length;
}
bis.close();
}
System.out.println(all);
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
private static long StrIOFilesTime() throws IOException
{
File [] files=GiveFiles.get();
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
int all=0;
for (File file : files)
{
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file)));
String temp="";
while((temp=br.readLine()) !=null)
{
all +=temp.length();
}
br.close();
}
System.out.println(all);
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
大文件测试
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
System.out.println("StreamIOFilesTime\t" + StreamIOFilesTime());
System.out.println("StrIOFilesTime\t" + StrIOFilesTime());
System.out.println("RandomIOFilesTime\t" + RandomIOFilesTime());
}
private static long RandomIOFilesTime() throws IOException
{
File [] files=GiveFiles.get();
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
int all=0;
for (File file : files)
{
byte [] temp=new byte[1024];
int length=0;
RandomAccessFile rfile=new RandomAccessFile(file, "r");
while((length=rfile.read(temp)) > 0)
{
all +=length;
}
rfile.close();
}
System.out.println(all);
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
private static long StreamIOFilesTime() throws IOException
{
File [] files=GiveFiles.get();
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
int all=0;
for (File file : files)
{
int length=0;
BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
byte [] temp=new byte[1024];
while((length=bis.read(temp)) > 0)
{
all +=length;
}
bis.close();
}
System.out.println(all);
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
private static long StrIOFilesTime() throws IOException
{
File [] files=GiveFiles.get();
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
int all=0;
for (File file : files)
{
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file)));
String temp="";
while((temp=br.readLine()) !=null)
{
all +=temp.length();
}
br.close();
}
System.out.println(all);
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
注意事项当然在本实例中没有考虑到小文件写成大文件的过程中花费的时间以及小文件压缩为大文件过程中花费的时间。只考虑了几种常见的格式,还有内存映射文件等等没有考虑进来,读取的方式也不考虑没有缓冲区的情况经验内容仅供参考,如果您需解决具体问题(尤其法律、医学等领域),建议您详细咨询相关领域专业人士。作者声明:本教程系本人依照真实经历原创,未经许可,谢绝转载。
- 评论列表(网友评论仅供网友表达个人看法,并不表明本站同意其观点或证实其描述)
-
